windows照片查看器内存不足的解决办法:首先打开电脑的系统属性,找到高级系统设置;然后点击高级,找到环境变量并点击;接着在用户变量中找到TMP;最后保存路径即可。

本文操作环境:Windows7系统,Dell G3电脑。
windows照片查看器内存不足的解决办法:
1、首先打开电脑的系统属性,然后在系统属性中找到高级系统设置
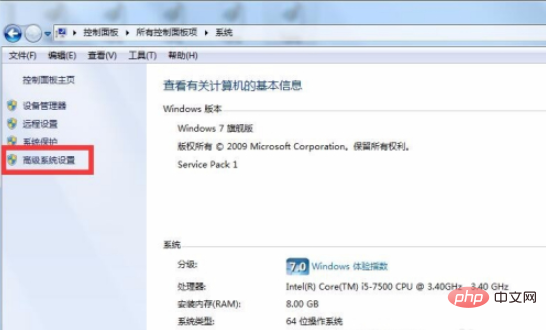
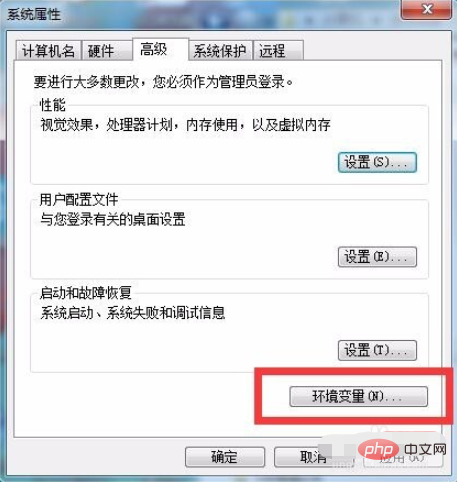
2、打开系统高级设置后,点击高级,然后找到环境变量,点击环境变量
3、然后找哦打用户变量,在用户变量中找到TMP,双击TMP,可以看到新的弹框
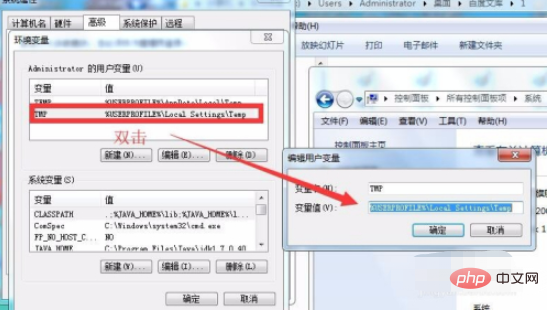
4、首先把原来的路径复制下来保存在txt中备用,防止修改失败,然后在新的弹框中输入一个系统的路径,这里我写的是D盘的tmp目录,然后点击确定
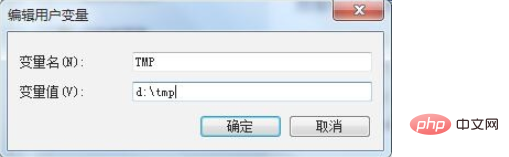
5、然后你再打开原有的照片,发现已经可以正常使用了
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END