1、开启电脑,在出现滚动的小圆圈的时候按住电源键强制关机,重复此操作2到3次,直到出现“选择一个选项”界面“,点击“疑难解答”选项
2、点击“重置此电脑”选项

3、点击“保留我的文件”,也可以选择“删除所有内容”(仅系统盘操作,不影响其他盘)
4、在电脑自动重启后,我们进入显示的账户

5、然后我们输入账户密码,点击“继续”
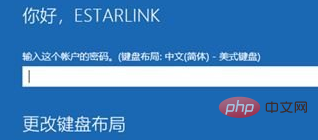
6、确认提示信息无误后,点击“重置”

7、最后等待电脑自动重启完成即可

推荐教程:windows教程
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END