
windows7把c盘东西移动到d盘的方法
1、win7 系统,电脑打开C盘。
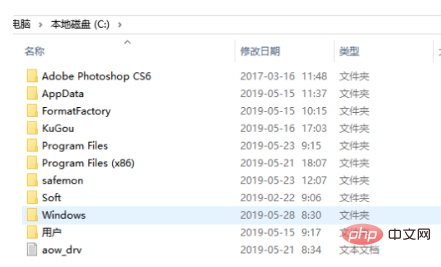
2、打开C盘后,找到要移动的文件,选中文件点击鼠标右键。
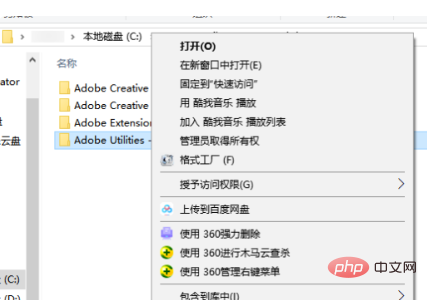
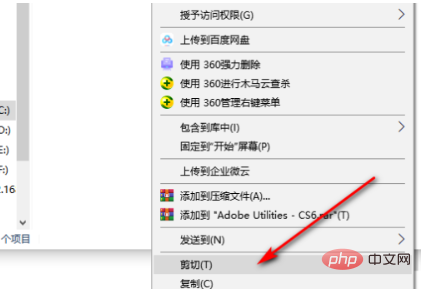
3、点击鼠标右键后,选中剪切选项。
4、把文件剪切之后,打开电脑D盘。
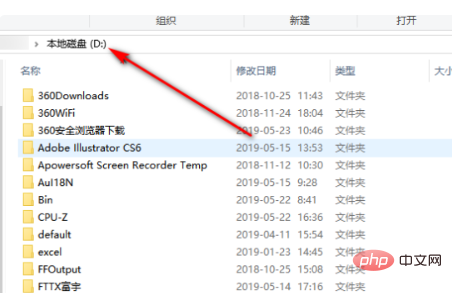
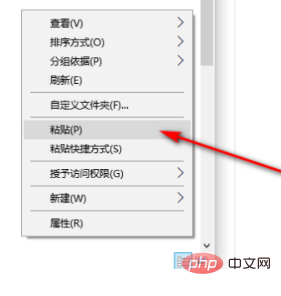
5、打开D盘后,鼠标右键点击空白处,然后选择粘贴就可以,等待移动就可以了。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


windows7把c盘东西移动到d盘的方法
1、win7 系统,电脑打开C盘。

2、打开C盘后,找到要移动的文件,选中文件点击鼠标右键。

3、点击鼠标右键后,选中剪切选项。

4、把文件剪切之后,打开电脑D盘。

5、打开D盘后,鼠标右键点击空白处,然后选择粘贴就可以,等待移动就可以了。
