方法一:重置internet explorer设置
打开IE浏览器,找到【工具】图标,打开【Internet 选项】
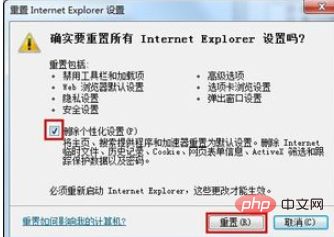
选择【高级】,点击【重置】,然后勾选【删除个性化设置】,点击【重置】,后续按提示操作即可
方法二:注册DLL组件
使用快捷键“Win+R”弹出【运行】,输入“cmd”,点击【确定】:
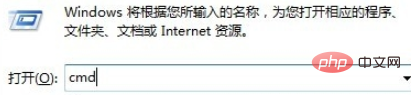
在命令提示符下输入:
for %1 in (%windir%system32*.dll) do regsvr32.exe /s %1
如果怕输入错误的话,可以复制这条指令,然后在命令提示框按鼠标右键使用“粘贴”功能,然后回车。在飞速滚屏完全静止前,别着急启动其他程序,先耐心等一会儿。如果出现什么提示,就按确定。运行完之后你的问题就会解决了。

相关教程推荐:windows教程
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END
喜欢就支持一下吧
相关推荐