现在给电脑安装系统一般都是使用克隆安装,也就是我们所讲的镜象文件安装(ghost)安装。但很多时候,我们安装完后,会出现一些错误并不能进入桌面。
例如:
如果屏幕上出现Missing operating system或者只有一个点一直闪烁,然后就没有然后了,对于这两种情况分三步走。
1、将U盘制做成启动盘,可以使用大白菜或老毛桃等工具。
2、将制做好的U盘插入电脑,并将其设置成优先启动,会出现以下界面(不同的U盘制做工具,界面大同小异):

3、选择diskgenius分区工具,就会出现以下界面:
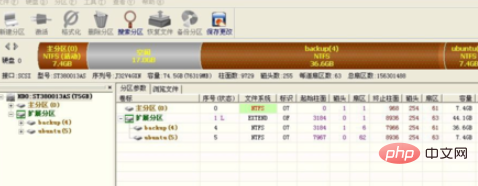
4、重建主引导记录MBR,然生重启。
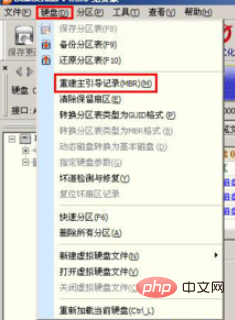
5、如果第一种不行,就将第一个分区的数据清除。选择我们C盘,然后点击“工具 – 清除扇区数据”菜单项,程序弹出下列对话框
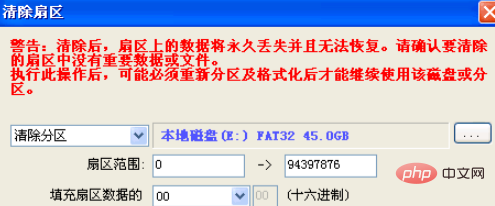
6、将C分区的数据清除,再重新安装系统,一般情况下可以解决90%的安装问题。
7、如果上面两种情况都不行,就只能直接安装,也就是硬装,不使用镜象文件。因为镜象文件在制做的过程过,或多或少的去除了一部分系统文件,安装是方便了,但是会造成少部份电脑不能正常安装,所以,我们就直接使用原文件进行安装。
8、我们可以先从网上下载我们所需系统的ISO文件(可以直接在百度上面搜关键词:windows xp iso或者win7 iso),然后用ultraiso工具将我们的U盘制做成启动盘。然后将U盘插入电脑,设置成从U盘启动就可以了。可以顺利的安装我们的系统。
相关文章教程推荐:windows教程
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END