0.前言
redis是KV型的内存数据库, 数据库存储的核心就是Hash表, 我们执行select命令选择一个存储的db之后, 所有的操作都是以hash表为基础的, 下面会分析下redis的hash数据结构和实现.
1.hash数据结构
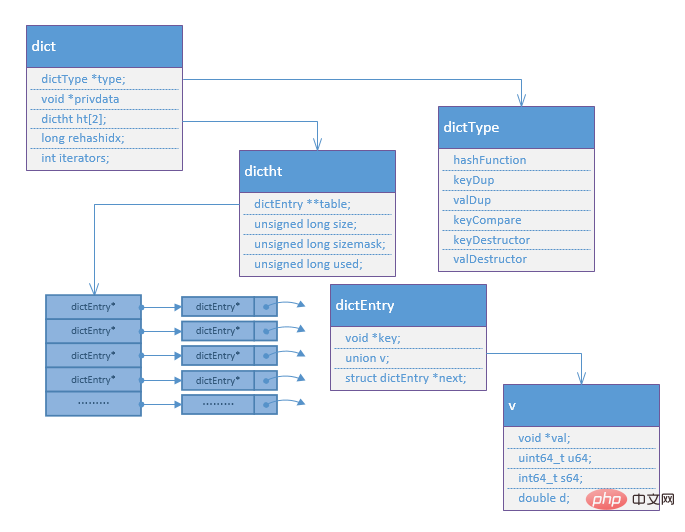
/*Hash表一个节点包含Key,Value数据对 */ typedef struct dictEntry { void *key; union { void *val; uint64_t u64; int64_t s64; double d; } v; struct dictEntry *next; /* 指向下一个节点, 链接表的方式解决Hash冲突 */ } dictEntry; /* 存储不同数据类型对应不同操作的回调函数 */ typedef struct dictType { unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj); } dictType; typedef struct dictht { dictEntry **table; /* dictEntry*数组,Hash表 */ unsigned long size; /* Hash表总大小 */ unsigned long sizemask; /* 计算在table中索引的掩码, 值是size-1 */ unsigned long used; /* Hash表已使用的大小 */ } dictht; typedef struct dict { dictType *type; void *privdata; dictht ht[2]; /* 两个hash表,rehash时使用*/ long rehashidx; /* rehash的索引, -1表示没有进行rehash */ int iterators; /* */ } dict;
2.hash数据结构图
3.渐进式hash说明
dict中ht[2]中有两个hash表, 我们第一次存储数据的数据时, ht[0]会创建一个最小为4的hash表, 一旦ht[0]中的size和used相等, 则dict中会在ht[1]创建一个size*2大小的hash表, 此时并不会直接将ht[0]中的数据copy进ht[0]中, 执行的是渐进式rehash, 即在以后的操作(find, set, get等)中慢慢的copy进去, 以后新添加的元素会添加进ht[0], 因此在ht[1]被占满的时候定能确保ht[0]中所有的数据全部copy到ht[1]中.
4.创建hash表
创建hash表过程非常简单,直接调用dictCreate函数, 分配一块内存,初始化中间变量即可.
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, void *privDataPtr) { /*分配内存*/ dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d)); /*初始化操作*/ _dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr); return d; }
5.添加元素
hash表中添加元素,首先判断空间是否足够, 然后计算key对应的hash值, 然后将需要添加的key和value放入表中.
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val) { /*添加入hash表中, 返回新添加元素的实体结构体*/ dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key); if (!entry) return DICT_ERR; /*元素val值放入元素实体结构中*/ dictSetVal(d, entry, val); return DICT_OK; } /* *添加元素实体函数 */ dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key) { int index; dictEntry *entry; dictht *ht; if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); /*根据key值计算新元素在hash表中的索引, 返回-1则表示元素已存在, 直接返回NULL*/ if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1) return NULL; /*如果在进行rehash过程,则新元素添加到ht[1]中, 否则添加到ht[0]中 */ ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0]; entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry)); entry->next = ht->table[index]; ht->table[index] = entry; ht->used++; /*设置元素key*/ dictSetKey(d, entry, key); return entry; } /* *计算索引的函数 */ static int _dictKeyIndex(dict *d, const void *key) { unsigned int h, idx, table; dictEntry *he; /* 判断hash表是否空间足够, 不足则需要扩展 */ if (_dictExpandIfNeeded(d) == DICT_ERR) return -1; /* 计算key对应的hash值 */ h = dictHashKey(d, key); for (table = 0; table ht[table].sizemask; /*遍历冲突列表, 判断需要查找的key是否已经在冲突列表中*/ he = d->ht[table].table[idx]; while(he) { if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) return -1; he = he->next; } if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break; } return idx; } /* *判断hash表是否需要扩展空间 */ static int _dictExpandIfNeeded(dict *d) { /*redis的rehash采用的渐进式hash, rehash时分配了原来两倍的内存空间, 在rehash阶段空间必定够用*/ if (dictIsRehashing(d)) return DICT_OK; /* hash表是空的需要初始化空间, 默认是4*/ if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return dictExpand(d, DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE); /* 已使用空间满足不了设置的条件*/ if (d->ht[0].used >= d->ht[0].size && (dict_can_resize || d->ht[0].used/d->ht[0].size > dict_force_resize_ratio)) { /*扩展空间, 使用空间的两倍*/ return dictExpand(d, d->ht[0].used*2); } return DICT_OK; } /* *扩展空间或者初始化hash表空间 */ int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size) { dictht n; /* 对需要分配大小圆整为2的倍数 */ unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size); /* 如果空间足够则表明调用错误 */ if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size) return DICT_ERR; n.size = realsize; n.sizemask = realsize-1; n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*)); n.used = 0; /*hash表为空初始化hash表*/ if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) { d->ht[0] = n; return DICT_OK; } /*新分配的空间放入ht[1], 后面一步一步进行rehash*/ d->ht[1] = n; d->rehashidx = 0; return DICT_OK; }
6.查找元素
查找元素过程,首先计算hash值, 然后计算在ht[0]和ht[1]中索引位置, 进行查找.
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key) { dictEntry *he; unsigned int h, idx, table; if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return NULL; /*如果正在进行rehash, 执行一次rehash*/ if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); h = dictHashKey(d, key); /*由于可能正在rehash, 因此要从ht[0]和ht[1]中分别进行查找, 找不到返回NULL*/ for (table = 0; table ht[table].sizemask; he = d->ht[table].table[idx]; /*遍历冲突列表查找元素*/ while(he) { if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) return he; he = he->next; } if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL; } return NULL; }
7.删除元素
删除元素首先查找元素, 然后将元素从hash表中移除即可, 调用dictDelete删除元素, 会同时删除元素所占空间
int dictDelete(dict *ht, const void *key) { return dictGenericDelete(ht,key,0); } static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) { unsigned int h, idx; dictEntry *he, *prevHe; int table; if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR; if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); h = dictHashKey(d, key); for (table = 0; table ht[table].sizemask; he = d->ht[table].table[idx]; prevHe = NULL; /*查找元素到元素,进行删除操作, 并释放占用的内存*/ while(he) { if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) { /* Unlink the element from the list */ if (prevHe) prevHe->next = he->next; else d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next; if (!nofree) { dictFreeKey(d, he); dictFreeVal(d, he); } zfree(he); d->ht[table].used--; return DICT_OK; } prevHe = he; he = he->next; } if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break; } return DICT_ERR; /* not found */ }
hash命令
hash命令操作都比较简单,需要注意的是当我们创建hash表示默认存储结构,并不是dict,而是ziplist结构,可以参考redis之Ziplist数据结构,hash_max_ziplist_entries和hash_max_ziplist_value值作为阀值,hash_max_ziplist_entries表示一旦ziplist中元素数量超过该值,则需要转换为dict结构;hash_max_ziplist_value表示一旦ziplist中数据长度大于该值,则需要转换为dict结构。
更多Redis相关技术文章,请访问redis之Ziplist数据结构栏目进行学习!