使用游标数据
在一个游标被打开后,可以使用 FETCH 语句分别访问它的每一行。FETCH 指定检索什么数据(所需的列),检索出来的数据存储在什么地方。它还向前移动游标中的内部行指针,使下一条 FETCH 语句检索下一行(不重复读取同一行)。
第一个例子从游标中检索单个行(第一行):
输入:
create procedure processorders() BEGIN -- declare local variables declare o int; -- declare the cursor declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders: -- open the cursor open ordernumbers; -- get order number fetch ordernumbers into o; -- close the cursor close ordernumbers; end;
分析:其中 FETCH 用来检索当前行的 order_num 列(将自动从第一行开始)到一个名为 o 的局部声明的变量中。对检索出的数据不做任何处理。
在下一个例子中,循环检索数据,从第一行到最后一行:
输入:
create procedure processorders() BEGIN -- declare local variables declare done boolean default 0; declare o int; -- declare the cursor declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders: --declare continue handler declare continue handler for sqlstate '02000' set done = 1; -- open the cursor open ordernumbers; --loop through all rows repeat -- get order number fetch ordernumbers into o; -- end of loop until done end repeat; -- close the cursor close ordernumbers; end;
分析:与前一个例子一样,这个例子使用 FETCH 检索当前 order_num到声明的名为 o 的变量中。但与前一个例子不一样的是,这个例子中的 FETCH 是在 REPEAT 内,因此它反复执行直到 done 为真(由 UNTILdone END REPEAT; 规定)。为使它起作用,用一个 DEFAULT 0 (假,不结束)定义变量 done 。那么, done 怎样才能在结束时被设置为真呢?答案是用以下语句:
declare continue handler for sqlstate '02000' set done = 1;
这条语句定义了一个 CONTINUE HANDLER ,它是在条件出现时被执行的代码。这里,它指出当 SQLSTATE ‘02000’ 出现时, SET done=1。SQLSTATE ‘02000’ 是一个未找到条件,当 REPEAT 由于没有更多的行供循环而不能继续时,出现这个条件。
MySQL的错误代码 关于MySQL 5使用的MySQL错误代码列表,请参阅http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/error-handling.html。
DECLARE 语句的次序 DECLARE 语句的发布存在特定的次序。用 DECLARE 语句定义的局部变量必须在定义任意游标或句柄之前定义,而句柄必须在游标之后定义。不遵守此顺序将产生错误消息。
如果调用这个存储过程,它将定义几个变量和一个 CONTINUE HANDLER ,定义并打开一个游标,重复读取所有行,然后关闭游标。如果一切正常,你可以在循环内放入任意需要的处理(在 FETCH 语句之后,循环结束之前)。
重复或循环? 除这里使用的 REPEAT 语句外,MySQL还支持循环语句,它可用来重复执行代码,直到使用 LEAVE 语句手动退出为止。通常 REPEAT 语句的语法使它更适合于对游标进行循环。
为了把这些内容组织起来,下面给出我们的游标存储过程样例的更进一步修改的版本,这次对取出的数据进行某种实际的处理:
输入:
create procedure processorders() BEGIN -- declare local variables declare done boolean default 0; declare o int; declare t decimal(8,2); -- declare the cursor declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders; -- declare continue handler declare continue handler for sqlstate '02000' set done = 1; -- create a table to store the results create table if not exists ordertotals (order_num int, total decimal(8,2)); -- open the cursor open ordernumbers; -- loop through all rows repeat -- get order number fetch ordernumbers into o; -- get the total for this order call ordertotal(o,1,t); -- insert order and total into ordertotals insert into ordertotals(order_num,total) values(o,t); -- end of loop until done end repeat; -- close the cursor close ordernumbers; END;
分析:在这个例子中,我们增加了另一个名为 t 的变量(存储每个订单的合计)。此存储过程还在运行中创建了一个新表(如果它不存在的话),名为 ordertotals 。这个表将保存存储过程生成的结果。 FETCH像以前一样取每个 order_num ,然后用 CALL 执行另一个存储过程(我们在前一章中创建)来计算每个订单的带税的合计(结果存储到 t )。最后,用 INSERT 保存每个订单的订单号和合计。
此存储过程不返回数据,但它能够创建和填充另一个表,可以用一条简单的 SELECT 语句查看该表:
输入:
select * from ordertotals;
输出:
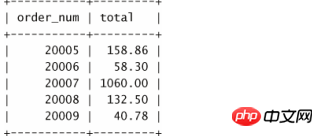
这样,我们就得到了存储过程、游标、逐行处理以及存储过程调用其他存储过程的一个完整的工作样例。



















