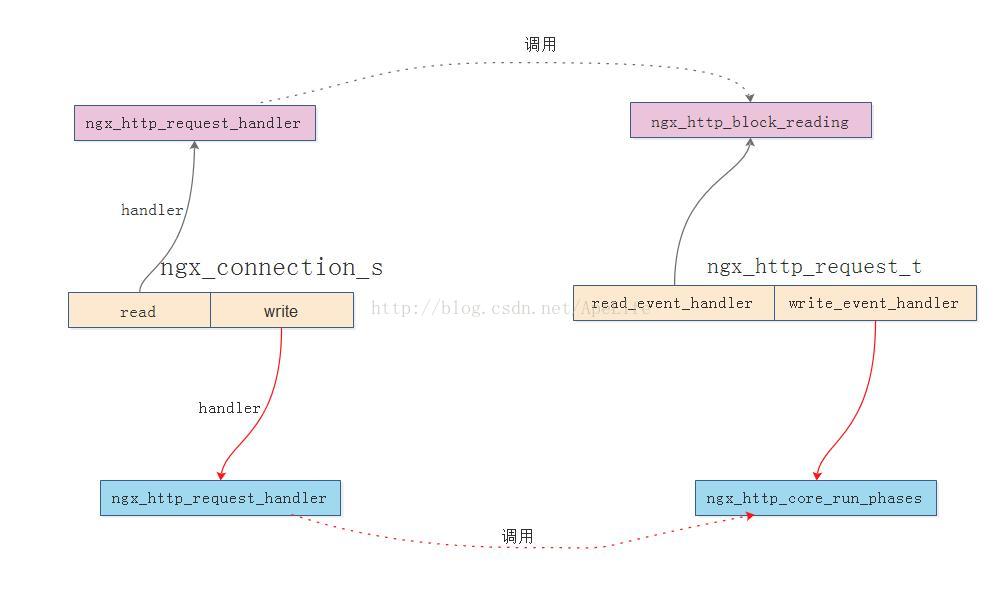
在接收完http请求行、http请求头部后,会调用ngx_http_process_request这个函数开始处理http请求。因为一个http请求由11个处理阶段组成,而每一个处理阶段都允许多个http模块介入,因此在这个函数中,将调度各个阶段的http模块共同完成这个请求。
//接收到http请求行与请求头后,http的处理流程,是第一个http处理请求的读事件回调 //这个函数执行后,将把读写事件的回调设置为ngx_http_request_handler。这样下次再有事件时 //将调用ngx_http_request_handler函数来处理,而不会再调用ngx_http_process_request了 static void ngx_http_process_request(ngx_http_request_t *r) { ngx_connection_t *c; c = r->connection; //因为已经接收完http请求行、请求头部了,准备调用各个http模块处理请求了。 //因此需要接收任何来自客户端的读事件,也就不存在接收http请求头部超时问题 if (c->read->timer_set) { ngx_del_timer(c->read); } //重新设置当前连接的读写事件回调 c->read->handler = ngx_http_request_handler; c->write->handler = ngx_http_request_handler; //设置http请求对象的读事件回调,这个回调不做任何的事情。 //那http请求对象的读事件回调,与上面的连接对应的读事件回调有什么关系呢? //当读事件发生后,连接对应的读事件回调ngx_http_request_handler会被调用, //在这个回调内会调用http请求对象的读事件回调ngx_http_block_reading,而这个回调是 //不会做任何事件的,因此相当于忽略了读事件。因为已经接收完了请求行请求头,现在要做的是调用各个http模块, //对接收到的请求行请求头进行处理 r->read_event_handler = ngx_http_block_reading; //调用各个http模块协同处理这个请求 ngx_http_handler(r); //处理子请求 ngx_http_run_posted_requests(c); }
ngx_http_process_request函数只会被调用一次。如果一次调度并不能处理完11个http阶段,那会将连接对象对应的读事件、写事件回调设置为ngx_http_request_handler。而请求对象的读事件设置为ngx_http_block_reading, 请求对象的写事件回调设置为ngx_http_core_run_phases, 这个回调在ngx_http_handler内设置。这样在事件再次到来时不会调用
ngx_http_process_request函数处理了。那event事件模块的读写事件回调与http请求对象的读写事件回调有什么关系呢?
//http请求处理读与写事件的回调,在ngx_http_process_request函数中设置。 //这个函数中将会调用http请求对象的读写事件回调。将event事件模块与http框架关联起来 static void ngx_http_request_handler(ngx_event_t *ev) { //如果同时发生读写事件,则只有写事件才会触发。写事件优先级更高 if (ev->write) { r->write_event_handler(r); //在函数ngx_http_handler设置为:ngx_http_core_run_phases } else { r->read_event_handler(r); //在函数ngx_http_process_request设置为:ngx_http_block_reading } //处理子请求 ngx_http_run_posted_requests(c); }
可以看到,连接对象的读事件回调中,会调用http请求对象的读事件回调。连接对象的写事件回调会调用http请求对象的写事件回调。
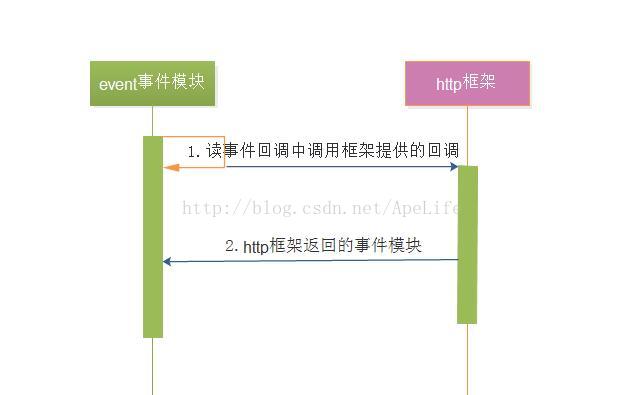
图中可看出,在event的读事件发生时,epoll返回后会调用读事件的回调ngx_http_request_handler。在这个读事件回调中,又会调用http框架,也就是http请求对象的读事件回调ngx_http_block_reading,这个http请求对象的读事件回调是不做任何事情的,相当于忽略读事件。因此http框架将会返回到事件模块。那为什么要忽略读事件呢?因为http请求行、请求头部都已经全部接收完成了, 现在要做的是调度各个http模块共同协作,完成对接收到的请求行,请求头部的处理。因此不需要接收来自客户端任何数据了。
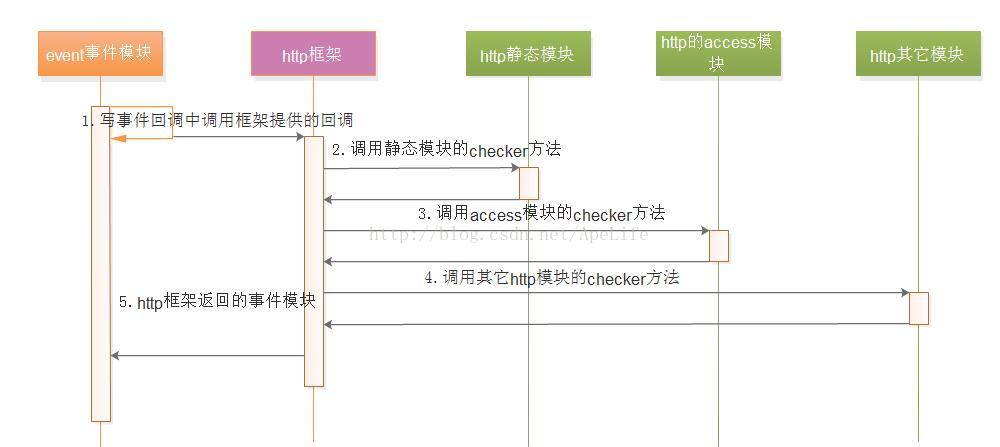
对于写事件的处理就复杂多了, 在event的写事件发生时,epoll返回后会调用写事件的回调ngx_http_request_handler,在这个写事件回调中,又会调用http框架,也就是http请求对象的写事件回调ngx_http_core_run_phases。这个http框架的回调会调度介入11个请求阶段的各个http模块的hander方法,共同完成http请求。
二、调度http模块处理请求
在上面代码中,会调度ngx_http_core_run_phases这个函数,使得各个http模块能介入到http请求中来。而这个函数是在ngx_http_handler设置的。
//调用各个http模块协同处理这个请求 void ngx_http_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r) { //不需要进行内部跳转。什么是内部跳转? 例如有个location结构,里面的 // if (!r->internal) { //将数组序号设为0,表示从数组第一个元素开始处理http请求 //这个下标很重要,决定了当前要处理的是11个阶段中的哪一个阶段, //以及由这个阶段的哪个http模块处理请求 r->phase_handler = 0; } else { //需要做内部跳转 cmcf = ngx_http_get_module_main_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); //将序号设置为server_rewrite_index r->phase_handler = cmcf->phase_engine.server_rewrite_index; } //设置请求对象的写事件回调,这个回调将会调度介入11个http阶段的各个http模块 //共同完成对请求的处理 r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_core_run_phases; //开始调度介入11个http阶段的各个http模块 ngx_http_core_run_phases(r); }
而ngx_http_core_run_phases函数就很简单了,调度介入11个http处理阶段的所有http模块的checker方法。
//调用各个http模块协同处理这个请求, checker函数内部会修改phase_handler void ngx_http_core_run_phases(ngx_http_request_t *r) { cmcf = ngx_http_get_module_main_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module); ph = cmcf->phase_engine.handlers; //调用各个http模块的checker方法,使得各个http模块可以介入http请求 while (ph[r->phase_handler].checker) { rc = ph[r->phase_handler].checker(r, &ph[r->phase_handler]); //从http模块返回ngx_ok,http框架则会把控制全交还给事件模块 if (rc == ngx_ok) { return; } }
假设阶段2有三个http模块介入了http请求, 阶段3有一个模块介入了http请求、阶段4也有一个模块介入了请求。当开始处理阶段2时,将调用阶段2中的所有http模块进行处理,此时phase_handler指向阶段2的开始位置。之后每处理完阶段2中的一个模块时,phase_handler指向阶段2的下一个模块,直到阶段2处理完成。
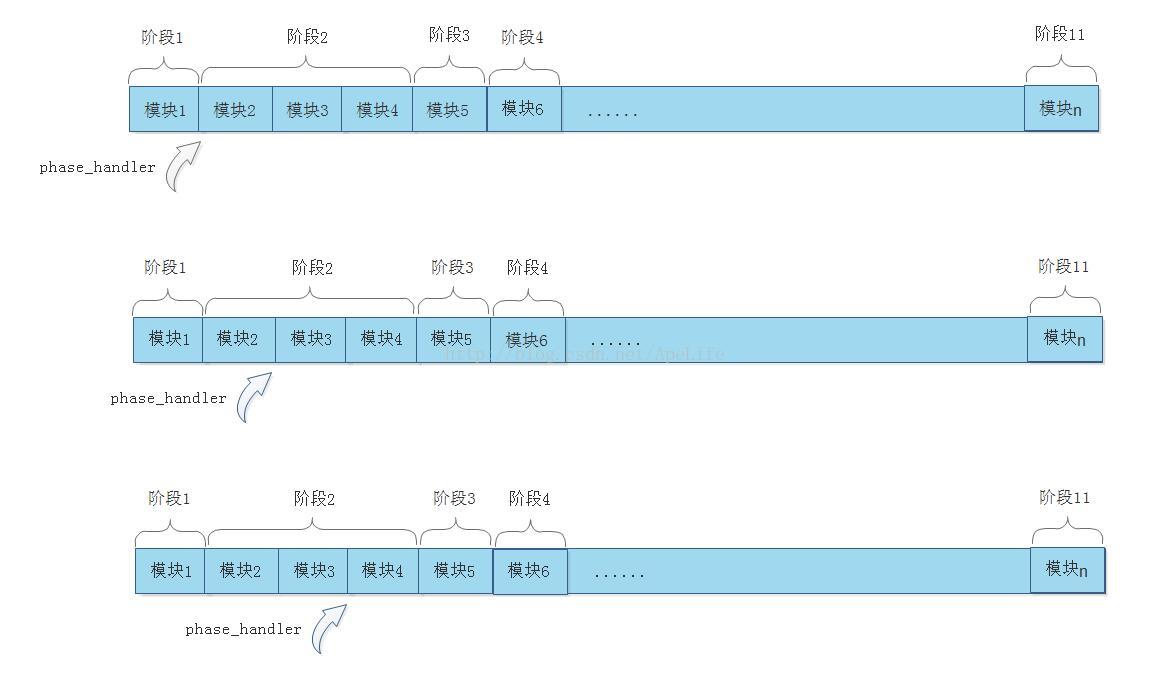
当阶段2中的所有http模块都处理完成时,phase_handler将指向阶段3
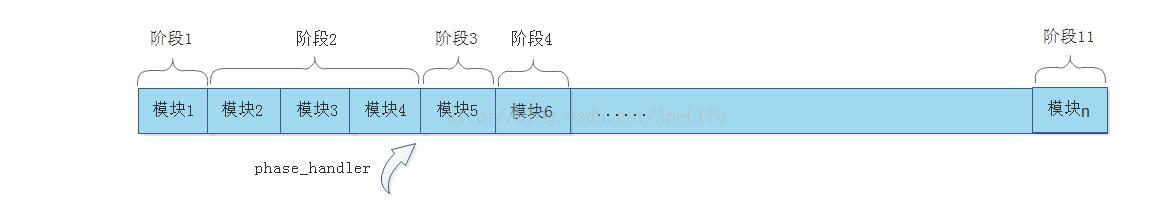
因阶段3只有一个http模块,因此当阶段3中的所有http模块都处理完成时,phase_handler将指向阶段4
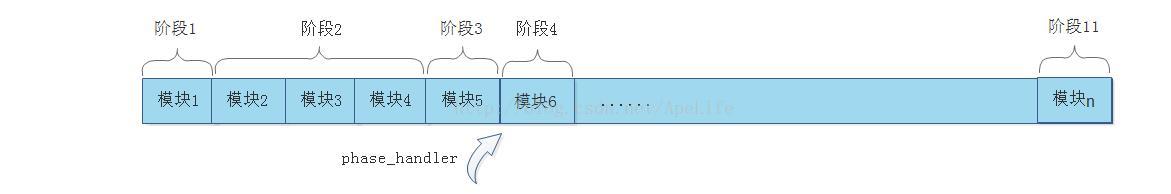
那这个handlers数组是什么时候创建的呢? 每一个http模块的checker回调又是做什么呢? 接下来将分析这两个问题
三、11个http请求阶段数组创建
在解析nginx.conf配置文件时,解析到http块时,会调用ngx_http_block这个函数开始解析http块。在这个函数中,也会把所有需要介入到11个http请求阶段的http模块,注册到数组中。
//开始解析http块 static char * ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) { //http配置解析完成后的后续处理,使得各个http模块可以介入到11个http阶段 for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) { if (ngx_modules[m]->type != ngx_http_module) { continue; } module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx; if (module->postconfiguration) { //每一个http模块的在这个postconfiguration函数中,都可以把自己注册到11个http阶段 if (module->postconfiguration(cf) != ngx_ok) { return ngx_conf_error; } } } }
例如ngx_http_static_module静态模块,会将自己介入11个http阶段的ngx_http_content_phase阶段回调设置为ngx_http_static_handler
//静态模块将自己注册到11个http请求阶段中的ngx_http_content_phase阶段 static ngx_int_t ngx_http_static_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) { cmcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module); h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[ngx_http_content_phase].handlers); //静态模块在ngx_http_content_phase阶段的处理方法 *h = ngx_http_static_handler; return ngx_ok; }
例如: ngx_http_access_module访问权限模块,会将自己介入11个http阶段的ngx_http_access_phase阶段回调设置为ngx_http_access_handler
//访问权限模块将自己注册到11个http请求阶段中的ngx_http_access_phase阶段 static ngx_int_t ngx_http_access_init(ngx_conf_t *cf) { cmcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module); h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[ngx_http_access_phase].handlers); //访问权限模块在ngx_http_access_phase阶段的处理方法 *h = ngx_http_access_handler; return ngx_ok; }
上面的这些操作,只是把需要介入到11个http阶段的http模块保存到了ngx_http_core_main_conf_t中的phases成员中,并没有保存到phase_engine中。那什么时候将phases的内容保存到phase_engine中呢? 还是在ngx_http_block函数中完成
//开始解析http块 static char * ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf) { //初始化请求的各个阶段 if (ngx_http_init_phase_handlers(cf, cmcf) != ngx_ok) { return ngx_conf_error; } }
假设阶段1有一个http模块介入请求,阶段2有三个http模块介入请求、阶段3也有一个http模块介入请求。则ngx_http_init_phase_handlers这个函数调用后,从ngx_http_phase_t phases[11]数组转换到ngx_http_phase_handler_t handlers数组的过程如下图所示:
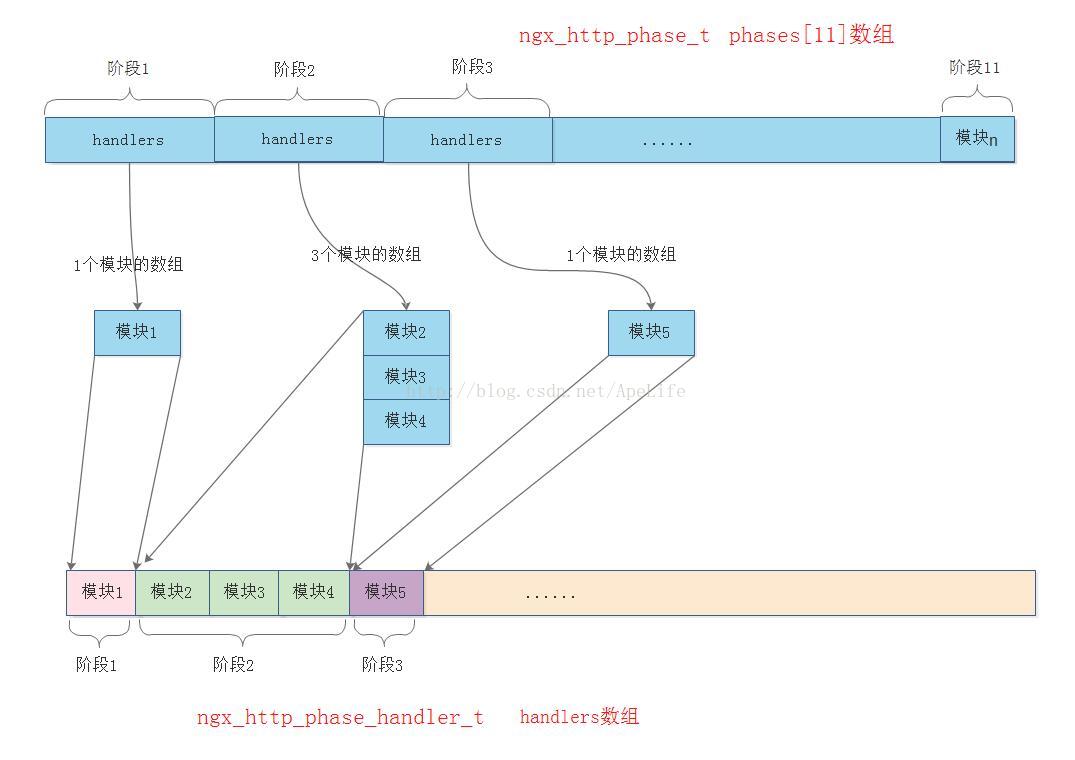
//初始化请求的各个阶段 static ngx_int_t ngx_http_init_phase_handlers(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf) { //11个http请求阶段,每一个阶段都可以有多个http模块介入。 //这里统计11个节点一共有多个少http模块。以便下面开辟空间 for (i = 0; i phases[i].handlers.nelts; } //开辟空间,存放介入11个处理阶段的所有http模块的回调 ph = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool,n * sizeof(ngx_http_phase_handler_t) + sizeof(void *)); cmcf->phase_engine.handlers = ph; n = 0; //对于每一个http处理阶段,给该阶段中所有介入的http模块赋值 for (i = 0; i phases[i].handlers.elts; switch (i) { case ngx_http_server_rewrite_phase://根据请求的uri查找location之前,修改请求的uri阶段 if (cmcf->phase_engine.server_rewrite_index == (ngx_uint_t) -1) { cmcf->phase_engine.server_rewrite_index = n; //重定向模块在数组中的位置 } checker = ngx_http_core_rewrite_phase; //每一个阶段的checker回调 break; case ngx_http_find_config_phase://根据请求的uri查找location阶段(只能由http框架实现) find_config_index = n; ph->checker = ngx_http_core_find_config_phase; n++; ph++; continue; case ngx_http_rewrite_phase: //根据请求的rui查找location之后,修改请求的uri阶段 if (cmcf->phase_engine.location_rewrite_index == (ngx_uint_t) -1) { cmcf->phase_engine.location_rewrite_index = n; } checker = ngx_http_core_rewrite_phase; break; case ngx_http_post_rewrite_phase: //ngx_http_rewrite_phase阶段修改rul后,防止递归修改uri导致死循环阶段 if (use_rewrite) { ph->checker = ngx_http_core_post_rewrite_phase; ph->next = find_config_index;//目的是为了地址重写后,跳转到ngx_http_find_config_phase阶段,根据 //url重写查找location n++; ph++; } continue; case ngx_http_access_phase: //是否允许访问服务器阶段 checker = ngx_http_core_access_phase; n++; break; case ngx_http_post_access_phase: //根据ngx_http_access_phase阶段的错误码,给客户端构造响应阶段 if (use_access) { ph->checker = ngx_http_core_post_access_phase; ph->next = n; ph++; } continue; case ngx_http_try_files_phase: //try_file阶段 if (cmcf->try_files) { ph->checker = ngx_http_core_try_files_phase; n++; ph++; } continue; case ngx_http_content_phase: //处理http请求内容阶段,大部分http模块最愿意介入的阶段 checker = ngx_http_core_content_phase; break; default: //ngx_http_post_read_phase, //ngx_http_preaccess_phase, //ngx_http_log_phase三个阶段的checker方法 checker = ngx_http_core_generic_phase; } n += cmcf->phases[i].handlers.nelts; //每一个阶段中所介入的所有http模块,同一个阶段中的所有http模块有唯一的checker回调, //但handler回调每一个模块自己实现 for (j = cmcf->phases[i].handlers.nelts - 1; j >=0; j--) { ph->checker = checker; ph->handler = h[j]; ph->next = n; ph++; } } return ngx_ok; }
四、http阶段的checker回调
在11个http处理阶段中,每一个阶段都有一个checker函数,当然有些阶段的checker函数是相同的。对每一个处理阶段,介入这个阶段的所有http模块都共用同一个checker函数。这些checker函数的作用是调度介入这个阶段的所有http模块的handler方法,或者切换到一下个http请求阶段。下面分析下ngx_http_post_read_phase,ngx_http_preaccess_phase,ngx_http_log_phase三个阶段的checker方法。
//ngx_http_post_read_phase, //ngx_http_preaccess_phase, //ngx_http_log_phase三个阶段的checker方法 //返回值: ngx_ok,http框架会将控制权交还给epoll模块 ngx_int_t ngx_http_core_generic_phase(ngx_http_request_t *r,ngx_http_phase_handler_t *ph) { ngx_int_t rc; //调用http模块的处理方法,这样这个http模块就介入到了这个请求阶段 rc = ph->handler(r); //跳转到下一个http阶段执行 if (rc == ngx_ok) { r->phase_handler = ph->next; return ngx_again; } //执行本阶段的下一个http模块 if (rc == ngx_declined) { r->phase_handler++; return ngx_again; } //表示刚执行的handler无法在这一次调度中处理完这一个阶段, //需要多次调度才能完成 if (rc == ngx_again || rc == ngx_done) { return ngx_ok; } //返回出错 /* rc == ngx_error || rc == ngx_http_... */ ngx_http_finalize_request(r, rc); return ngx_ok; }