一、nginx
nginx(“engine x”)是一款是由俄罗斯的程序设计师igor sysoev所开发高性能的 web和 反向代理 服务器,也是一个 imap/pop3/smtp 代理服务器。
三大WEB服务器:apache, Nginx, lighttpd之一。Nginx是一种很好的替代品,当需要处理高并发连接时,它比Apache服务器更为适合。
nginx应用场合
-
静态服务器。(图片,视频服务)另一个是lighttpd。并发几万,html,js,css,flv,jpg,gif等。
-
动态服务,nginx——fastcgi 的方式运行PHP,jsp。(PHP并发在500-1500,MySQL 并发在300-1500)。
-
反向代理,负载均衡。日pv2000W以下,都可以直接用nginx做代理。
-
缓存服务。类似 SQUID,VARNISH。
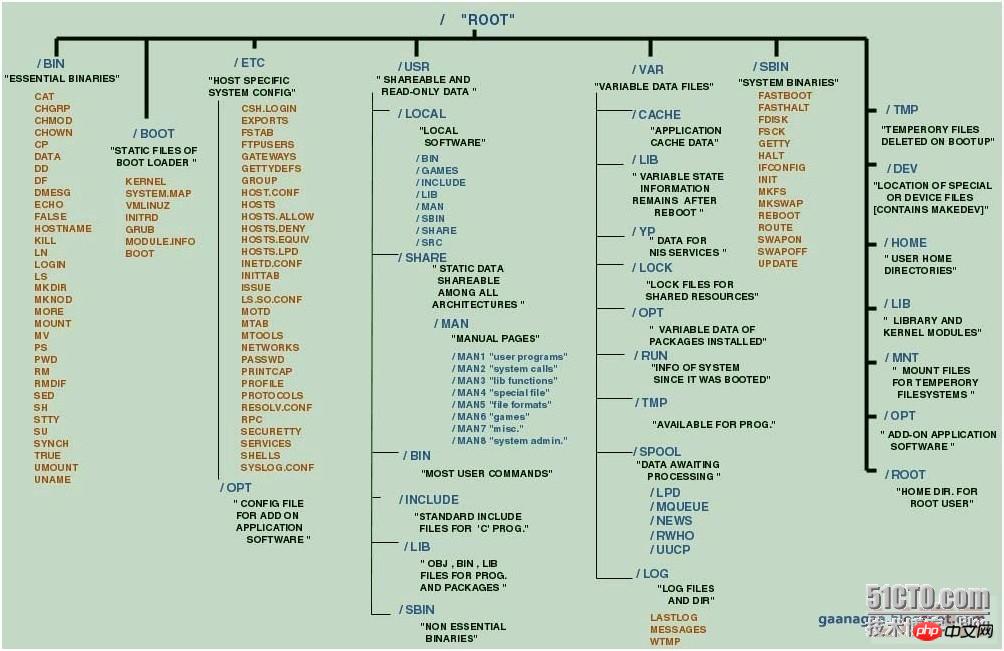
官网提供三种版本:
Nginx官网提供了三个类型的版本
Mainline version:Mainline 是 Nginx 目前主力在做的版本,可以说是开发版
Stable version:最新稳定版,生产环境上建议使用的版本
Legacy versions:遗留的老版本的稳定版
二、nginx服务搭建
1、使用apt安装
sudo apt install nginx
2、安装后的位置:
-
/usr/sbin/nginx:主程序
-
/etc/nginx:存放配置文件
-
/usr/share/nginx:存放静态文件
-
/var/log/nginx:存放日志
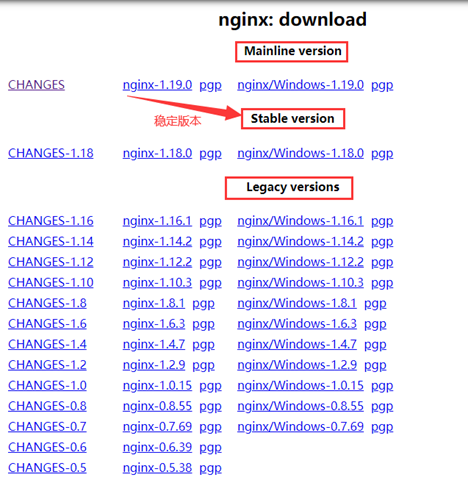
3、启动并验证效果
service nginx start # 启动nginx service nginx reload # 重新加载nginx配置文件
在浏览器输入你的ip地址,如果出现Wellcome to nginx 那么就是配置成功。
另外两个命令
nginx -s reopen # 重启 Nginx nginx -s stop # 停止 Nginx
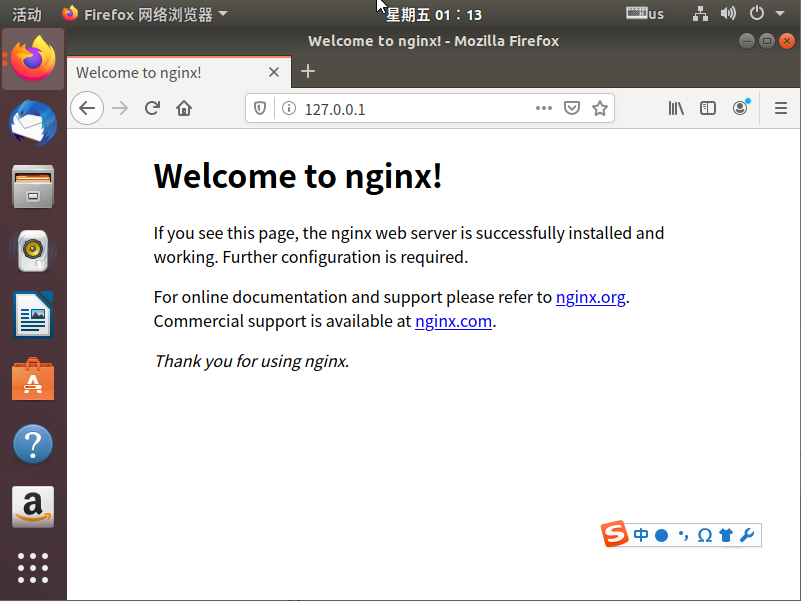
4、查看版本号:
~$ nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 (Ubuntu)
三、nginx配置文件介绍
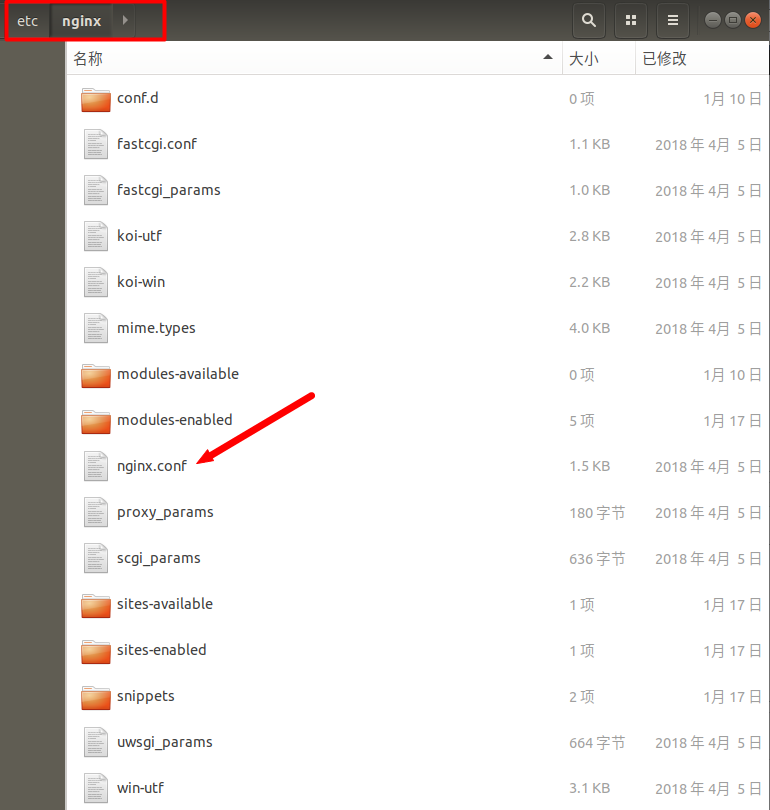
1、nginx 文件结构
-
全局块:配置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等。
-
events块:配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数,选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求,是否允许同时接受多个网路连接,开启多个网络连接序列化等。
-
http块:可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,mime-type定义,日志自定义,是否使用sendfile传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等。
-
server块:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。
-
location块:配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
... # 全局块。配置影响nginx全局的指令。 events { # events块。配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。 ... } http # http块。可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。 { ... # http全局块 server # server块。配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。 { ... # server全局块 location [PATTERN] # location块。配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。 { ... } location [PATTERN] { ... } } server { ... } ... # http全局块 }
2、默认的配置
## # You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding # of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx. # https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/ # https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/ # https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure # # In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and # leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be # updated by the nginx packaging team. # # This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other # applications, such as Drupal or Wordpress. These applications will be made # available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8. # # Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples. ## # Default server configuration # server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; # SSL configuration # # listen 443 ssl default_server; # listen [::]:443 ssl default_server; # # Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic. # See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332 # # Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration. # See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782 # # Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package # Don't use them in a production server! # # include snippets/snakeoil.conf; root /var/www/html; # Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; server_name _; location / { # First attempt to serve request as file, then # as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404. try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } # pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server # #location ~ .php$ { # include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf; # # # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets): # fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock; # # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets): # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /.ht { # deny all; #} } # Virtual Host configuration for example.com # # You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that # to sites-enabled/ to enable it. # #server { # listen 80; # listen [::]:80; # # server_name example.com; # # root /var/www/example.com; # index index.html; # # location / { # try_files $uri $uri/ =404; # } #}
3、nginx的基本配置
########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。################# #user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。 #worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1 #pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址 error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg events { accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off #use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512 } http { include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain #access_log off; #取消服务日志 log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式 access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值 sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。 sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。 keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。 upstream mysvr { server 127.0.0.1:7878; server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备 } error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页 server { keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。 listen 80; #监听端口 server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址 location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。 #root path; #根目录 #index vv.txt; #设置默认页 proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表 deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip } } }
四、 nginx虚拟主机配置
#下面是server虚拟主机的配置段 server { listen 80;#监听端口 server_name localhost;#域名 index index.html index.htm index.php; root /usr/local/webserver/nginx/html;#站点目录 location ~ .*.(php|php5)?$ { #fastcgi_pass unix:/tmp/php-cgi.sock; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; include fastcgi.conf; } location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ico)$ { expires 30d; #access_log off; } location ~ .*.(js|css)?$ { expires 15d; #access_log off; } access_log off; }
验证配置文件:
root@ubuntu: nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
五、nginx全局变量
-
为了记录客户端的IP地址,可以使用$remote_addr和$http_x_forwarded_for
-
$remote_user :用来记录客户端用户名称;
-
$time_local : 用来记录访问时间与时区;
-
$request : 用来记录请求的url与http协议;
-
$status : 用来记录请求状态;成功是200;
-
$body_bytes_s ent :记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;
-
$http_referer :用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的;
-
$http_user_agent :记录客户端浏览器的相关信息;
访问链接是:http://localhost:88/test1/test.php 网站路径是:/var/www/html $host:localhost $server_port:88 $request_uri:<a>http:</a>//localhost:88/test1/test.php $document_uri:/test1/test.php $document_root:/var/www/html $request_filename:/var/www/html/test1/test.php
六、Nginx主要配置
1、静态Http服务器配置
首先,Nginx是一个HTTP服务器,可以将服务器上的静态文件(如HTML、图片)通过HTTP协议展现给客户端。
配置:
server { listen 80; # 端口 server_name localhost 192.168.1.100; # 域名 location / { # 代表这是项目根目录 root /usr/share/nginx/www; # 虚拟目录 } }
2、反向代理服务器配置
什么是反向代理?
客户端本来可以直接通过HTTP协议访问某网站应用服务器,如果网站管理员在中间加上一个Nginx,客户端请求Nginx,Nginx请求应用服务器,然后将结果返回给客户端,此时Nginx就是反向代理服务器。
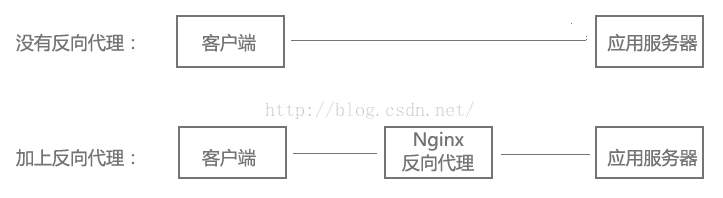
反向代理配置:
server { listen 80; location / { proxy_pass http://192.168.0.112:8080; # 应用服务器HTTP地址 } }
既然服务器可以直接HTTP访问,为什么要在中间加上一个反向代理,不是多此一举吗?反向代理有什么作用?继续往下看,下面的负载均衡、虚拟主机,都基于反向代理实现,当然反向代理的功能也不仅仅是这些。
3、负载均衡配置
当网站访问量非常大,也摊上事儿了。因为网站越来越慢,一台服务器已经不够用了。因此,可以将同一应用部署在多台服务器上,以将众多用户请求分配至多台机器进行处理。即使其中一台服务器故障,只要其他服务器正常运行,用户仍然可以正常使用,这是多台服务器带来的好处。Nginx可以通过反向代理来实现负载均衡。
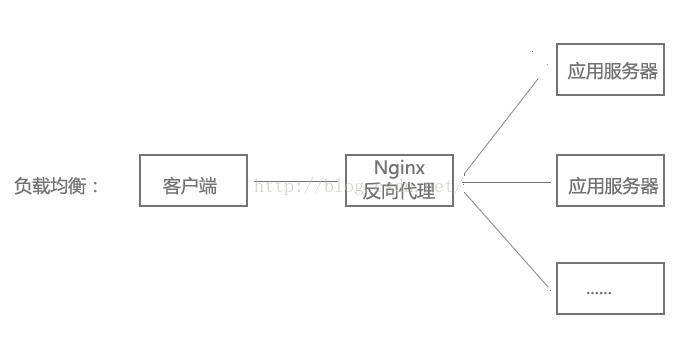
负载均衡配置:
upstream myapp { server 192.168.0.111:8080; # 应用服务器1 server 192.168.0.112:8080; # 应用服务器2 } server { listen 80; location / { proxy_pass http://myweb; } }
4、虚拟主机配置
有的网站访问量大,需要负载均衡。然而并不是所有网站都如此出色,有的网站,由于访问量太小,需要节省成本,将多个网站部署在同一台服务器上。
例如将www.aaa.com和www.bbb.com两个网站部署在同一台服务器上,两个域名解析到同一个IP地址,但是用户通过两个域名却可以打开两个完全不同的网站,互相不影响,就像访问两个服务器一样,所以叫两个虚拟主机。
虚拟主机配置:
server { listen 80 default_server; server_name _; return 444; # 过滤其他域名的请求,返回444状态码 } server { listen 80; server_name www.aaa.com; # www.aaa.com域名 location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; # 对应端口号8080 } } server { listen 80; server_name www.bbb.com; # www.bbb.com域名 location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:8081; # 对应端口号8081 } }
在服务器8080和8081分别开了一个应用,客户端通过不同的域名访问,根据server_name可以反向代理到对应的应用服务器。
虚拟主机的原理是通过HTTP请求头中的Host是否匹配server_name来实现的,有兴趣的同学可以研究一下HTTP协议。
另外,server_name配置还可以过滤有人恶意将某些域名指向你的主机服务器。